
U.S. Antibiotic Awareness Week

U.S. Antibiotic Awareness Week is an annual observance that raises awareness of the threat of antibiotic resistance and the importance of appropriate antibiotic use.
Antibiotic resistance is one of the most urgent threats to the public’s health. Each year in the United States, at least 2 million people get infected with antibiotic-resistant bacteria. At least 23,000 people die as a result.
What is an antibiotic?
Antibiotics, also known as antimicrobial drugs, are drugs that fight infections caused by bacteria in both humans and animals. Antibiotics fight these infections either by killing the bacteria or making it difficult for the bacteria to grow and multiply. Antibiotics only treat certain bacterial infections. Antibiotics do not have any effect on viruses.
Any time antibiotics are used, they can cause side effects and lead to antibiotic resistance.

How do bacteria become resistant to antibiotics?
Bacteria can become resistant to antibiotics through several ways. Some bacteria can “neutralize” an antibiotic by changing it in a way that makes it harmless. Others have learned how to pump an antibiotic back outside of the bacteria before it can do any harm. Some bacteria can change their outer structure so the antibiotic has no way to attach to the bacteria it is designed to kill.
After being exposed to antibiotics, sometimes one of the bacteria can survive because it found a way to resist the antibiotic. If even one bacterium becomes resistant to antibiotics, it can then multiply and replace all the bacteria that were killed off. That means that exposure to antibiotics provides selective pressure making the surviving bacteria more likely to be resistant. Bacteria can also become resistant through mutation of their genetic material.
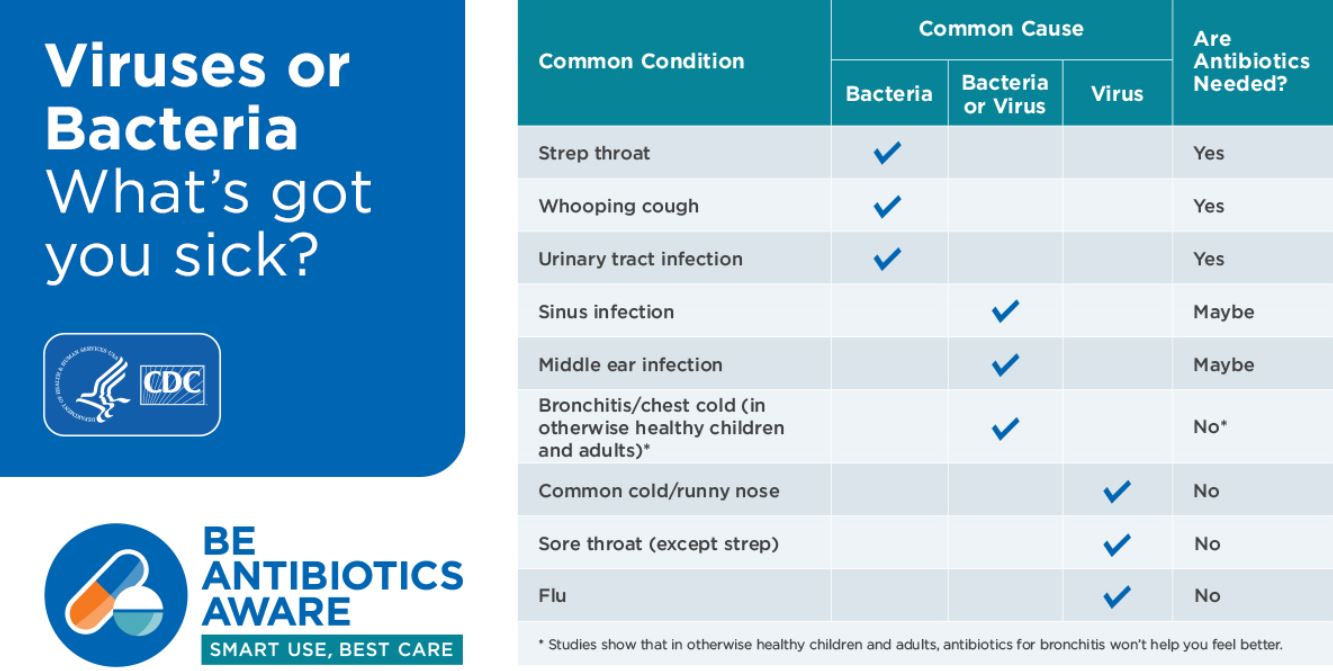
Which infections are caused by viruses and should not be treated with antibiotics?
Viral infections should not be treated with antibiotics. Common infections caused by viruses include:
- Colds
- Flu
- Most sore throats
How should I use antibiotics to protect myself and my community from antibiotic resistance?
Here is what you can do to help prevent antibiotic resistance:
- Tell your healthcare professional you are concerned about antibiotic resistance.
- Ask your healthcare professional if there are steps you can take to feel better and get symptomatic relief without using antibiotics.
- Take the prescribed antibiotic exactly as your healthcare professional tells you.
- Safely throw away leftover medication.
- Ask your healthcare professional about vaccines recommended for you and your family to prevent infections that may require an antibiotic.
- Never skip doses.
- Never take an antibiotic for a viral infection like a cold or the flu.
- Never pressure your healthcare professional to prescribe an antibiotic.
- Never save antibiotics for the next time you get sick.
- Never take antibiotics prescribed for someone else.

Source:
- CDC
Images:
- CDC


Most Commented